Fasciotomy: Lower Extremity
Fasciotomy: Lower Extremity
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Buttock Fasciotomy
Buttock Compartments (x3)
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Minimus
- Tensor Fascia Lata
Buttock Fasciotomy Technique
- Technique is Not Well Standardized
- Incision: Longitudinal Incision Over the Lateral Hip
- Releases All Three Muscle Compartments
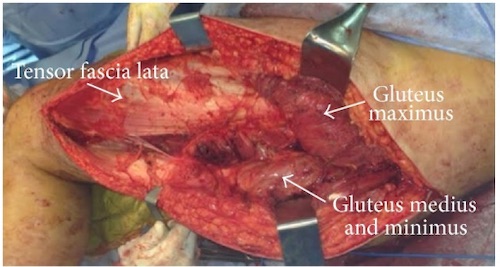
Buttock Fasciotomy 1
Thigh Fasciotomy
Thigh Compartments (x3)
- Anterior (Quadriceps and Sartorius)
- Posterior (Hamstring)
- Medial/Adductor
Thigh Fasciotomy Technique
- Incision: Longitudinal Skin Incision Over the Lateral Thigh
- Alternative: Can Make Two Separate Anterior/Posterior Incisions for Each Compartment Separately
- Release the Anterior and Posterior Compartments
- May Also Consider a Separate Medial/Adductor Incision
- Generally Omitted as the Medial Compartment Rarely Develops Compartment Syndrome
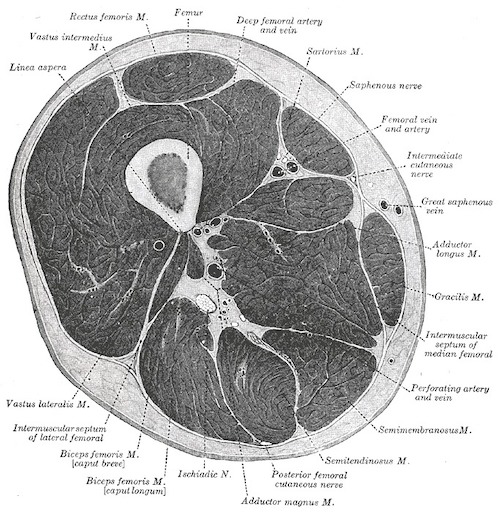
Thigh Compartments
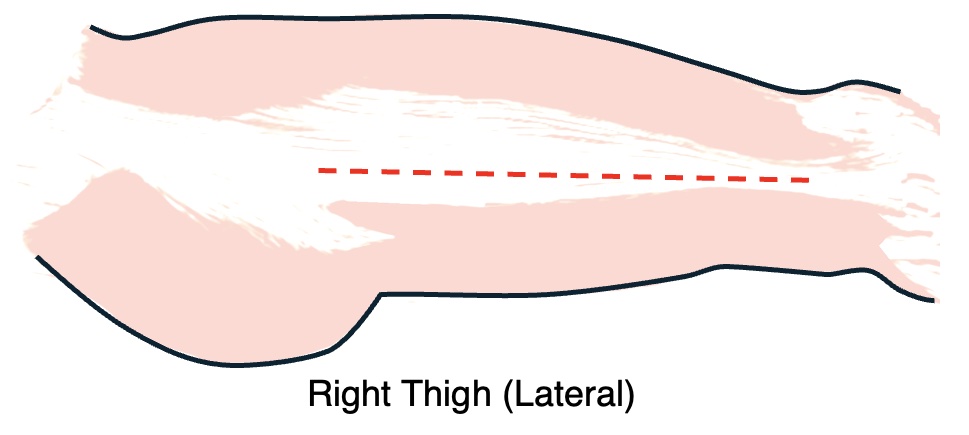
Thigh Fasciotomy
Calf Fasciotomy
The Most Commonly Performed Fasciotomy in Trauma
Calf Compartments (x4)
- Anterior
- Muscles: Tibialis Anterior, Extensor Hallucis Longus, and Extensor Digitorum Longus
- Vascular: Anterior Tibial Artery
- Nerve: Deep Peroneal Nerve (Dorsiflexion and First Webspace Sensation)
- Lateral
- Muscles: Peroneus Brevis and Peroneus Longus
- Nerve: Superficial Peroneal Nerve (Eversion and Lateral Foot Sensation)
- Deep Posterior
- Muscles: Tibialis Posterior, Flexor Hallucis Longus, and Flexor Digitorum Longus
- Vascular: Posterior Tibial Artery and Peroneal Artery
- Nerve: Tibial Nerve (Plantar Flexion)
- Superficial Posterior
- Muscles: Gastrocnemius and Soleus
- Nerve: Sural Nerve
The Anterior Compartment is the Most Commonly Affected Compartment and Generally the First to Be Affected (First Web Space Numbness is an Early Finding)
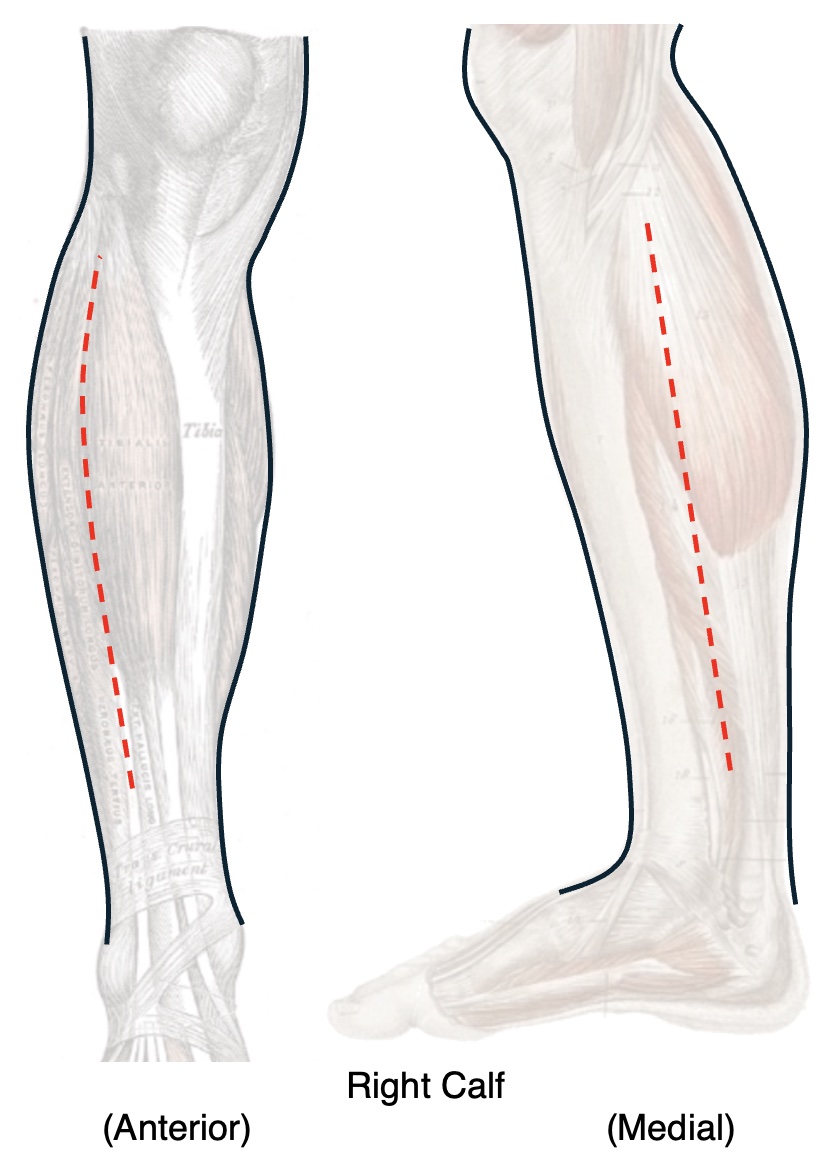
Calf Fasciotomy: Double-Incision Technique
- Most Common Approach – Easier to Access Deep Posterior Compartment
- Anterolateral Incision:
- 15-20 cm Vertical Incision Midway Between Tibia and Fibula
- Incise the Anterior Fascia Longitudinally – Just Anterior to the Intermuscular Septum
- Incise the Lateral Fascia Longitudinally – Just Posterior to the Intermuscular Septum
- Incise the Intermuscular Septum Transversely to Create an “H”
- *Protect Superficial Peroneal Nerve (Around the Neck of the Fibula) – Most Common Nerve Injured
- Posteromedial Incision:
- 15-20 cm Vertical Incision 1-2 cm Posterior to Posterior Border of Tibia
- Take Care to Avoid Saphenous Vein Injury
- Incise the Superficial Posterior Fascia Just Under the Skin Incision
- Detach the Soleus from the Tibia to Release the Deep Posterior Compartment
- 15-20 cm Vertical Incision 1-2 cm Posterior to Posterior Border of Tibia
Calf Fasciotomy: Single-Incision Technique
- Single Lateral Incision: 15-18 cm Vertical Incision Just Anterior to Fibula
- Directly Incise the Anterior and Lateral Compartments – Similar to the Anterolateral Incision of the Double-Incision Technique
- Incise the Anterior Fascia Longitudinally – Just Anterior to the Intermuscular Septum
- Incise the Lateral Fascia Longitudinally – Just Posterior to the Intermuscular Septum
- Incise the Intermuscular Septum Transversely to Create an “H”
- *Protect Superficial Peroneal Nerve (Around the Neck of the Fibula) – Most Common Nerve Injured
- Raise a Small Posterior Flap to Access and Incise the Superficial Posterior Compartment
- Reflect the Soleus from Fibula Through the Posterior Flap to Release the Deep Posterior Compartment
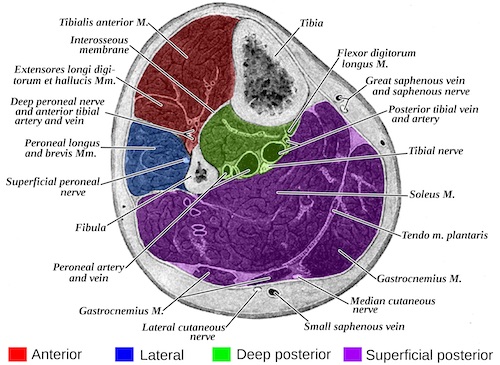
Calf Compartments
Calf Fasciotomy
Foot Fasciotomy
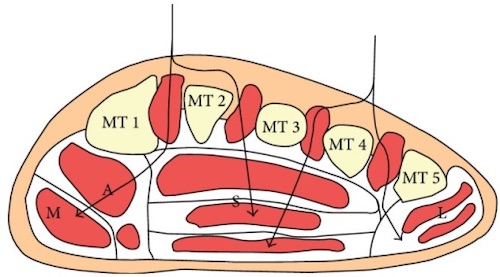
Foot Compartments (x4-9, Debated)
- Interosseous – May Be x4 Separate Compartments
- Medial
- Lateral
- Central – May Be x3 Separate Compartments (Superficial, Middle, and Deep)
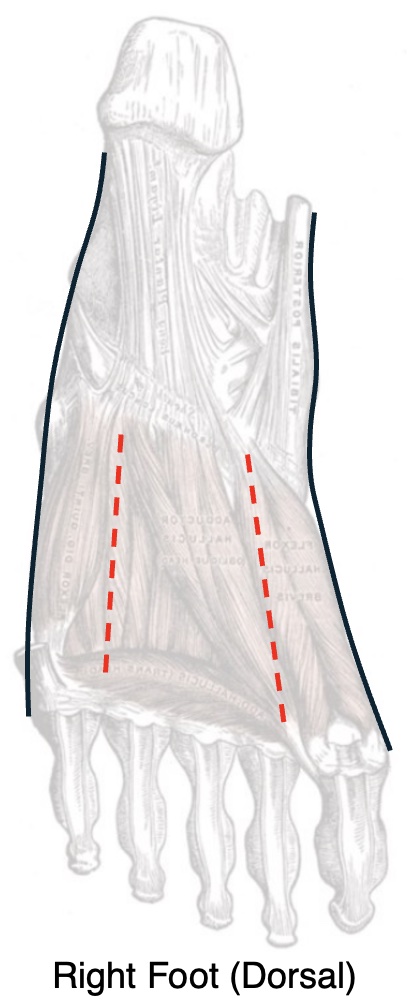
Foot Fasciotomy Technique
- Dual Dorsal Incisions:
- Medial Incision: Along Medial Margin of Second Metatarsal
- Releases the 1st/2nd Interosseous, Medial, and Deep Central Compartments
- Lateral Incision: Along Lateral Margin of Fourth Metatarsal
- Releases the 3rd/4th Interosseous, Lateral, Superficial Central, and Middle Central Compartments
- May Consider Adding a Medial Incision to Release the Calcaneal Compartment
Foot Fasciotomy
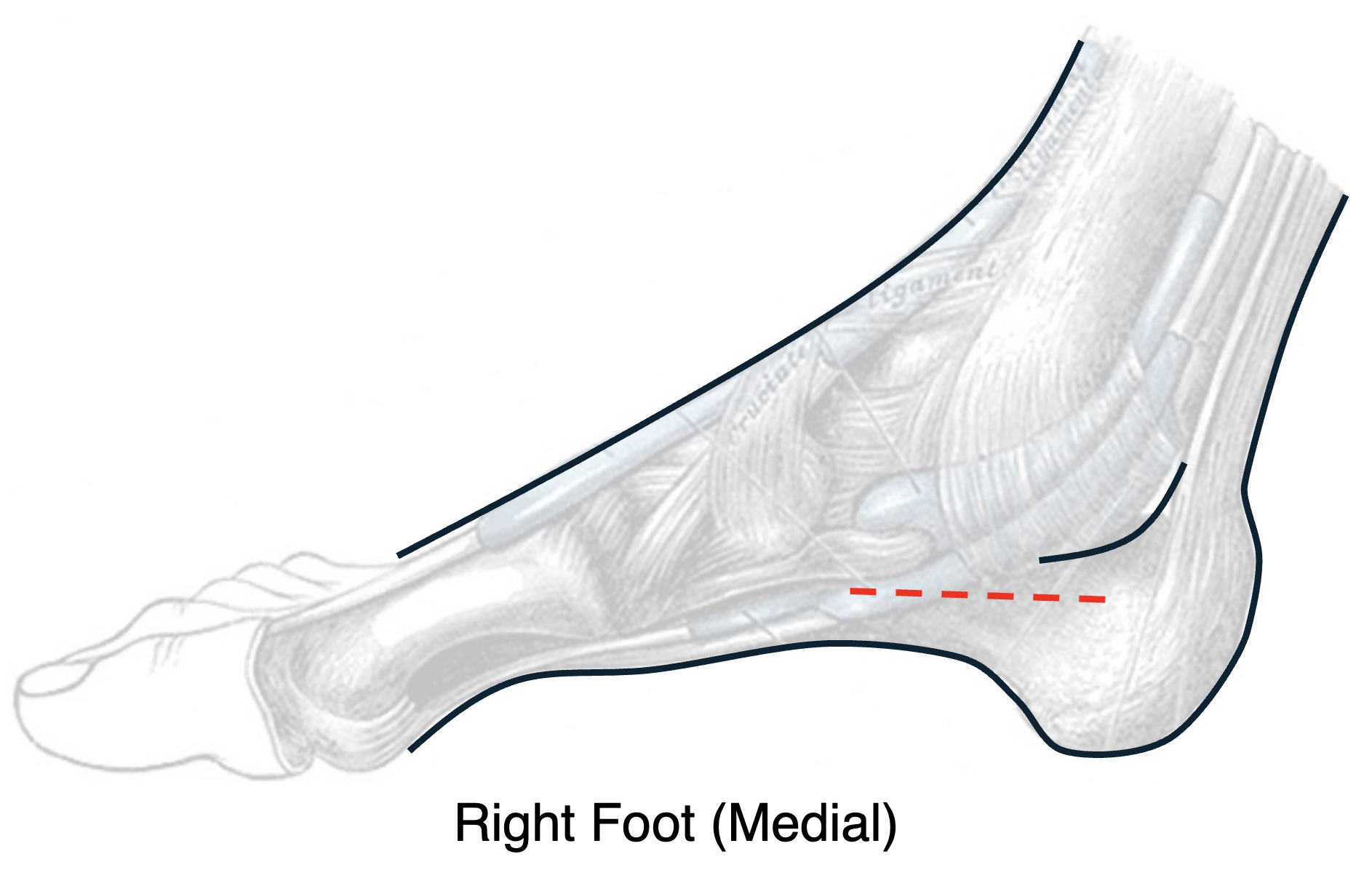
Foot Fasciotomy – Calcaneal Compartment Release
Foot Fasciotomy – Depth 2
References
- Diaz Dilernia F, Zaidenberg EE, Gamsie S, Taype Zamboni DE, Carabelli GS, Barla JD, Sancineto CF. Gluteal Compartment Syndrome Secondary to Pelvic Trauma. Case Rep Orthop. 2016;2016:2780295. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Raza H, Mahapatra A. Acute compartment syndrome in orthopedics: causes, diagnosis, and management. Adv Orthop. 2015;2015:543412. (License: CC BY-3.0)
