Wolf-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome
Wolf-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome
David Ray Velez, MD
A Pre-Excitation Syndrome Due to an Accessory AV Pathway Through the Bundle of Kent
EKG Pattern
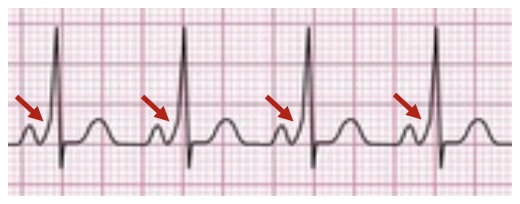
- Pre-Excitation “Delta Waves” (Slurring Slow Risk of the Initial QRS Complex)
- Short PR Interval (< 120 ms)
- Prolonged QRS Complex
Wolf-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome
Pathophysiology
- A Pre-Excitation Syndrome Due to an Accessory AV Pathway Through the Bundle of Kent
- Atrial Impulse Passes Through Both the AV Node and the Accessory Pathway
- The Accessory Pathway Conducts the Signal Faster but the Subsequent Ventricular Activation is Slower Since it is Not Through the Conducting System (Seen as a Delta Wave)
- May Cause Recurrent SVT
Treatment
- Unstable: Synchronized Cardioversion
- Stable: Procainamide
- Dosing: 15 mg/kg Total Dose at 20-50 mg/min
- Other Options: Flecainide, Ibutilide
- Avoid Drugs that Block the AV Node (β-Blockers, Calcium Channel Blockers, Digoxin) – These Can Cause Conversion to Ventricular Tachycardia or Ventricular Fibrillation
- Consider Catheter Ablation in the Chronic Management
- *See Antiarrhythmic Pharmacology
