Ventricular Fibrillation (VF/V-Fib)
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF/V-Fib)
David Ray Velez, MD
Ventricular Myocardium Depolarize Erratically in an Uncoordinated Manner
- Non-Perfusing Rhythm and Fatal if Not Corrected
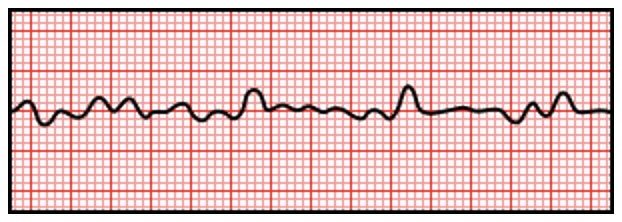
EKG Pattern
- Sudden Chaotic Irregular Deflections
- No Identifiable P Waves, QRS Complexes or T Waves
- Rate 150-500 bpm
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF/V-Fib)
Causes
- Myocardial Ischemia
- Cardiomyopathy
- Prolonged QT Syndrome
- Cardiac Tamponade
- Blunt Cardiac Injury
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pneumothorax
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Electrolyte Derangements
- Aspiration
- Sepsis
- Seizure
- Hypothermia
Treatment
- Follow ACLS Guidelines: *See Cardiac Arrest
- Start CPR Immediately and Give Oxygen
- Treat Any Reversible Causes
- Check Rhythm Every 2 Minutes
- Ventricular Fibrillation is a Shockable Rhythm
- Defibrillate
- Initial Dose: Biphasic 120-200 J
- Higher Subsequent Doses May Be Considered
- Drug Therapy:
- Epinephrine
- The First Agent Given
- Dose: 1 mg IV/IO
- Give Initially and Repeat Every 3-5 Minutes
- Amiodarone
- Dose: 300 mg (First Dose) and 150 mg (Second Dose)
- Generally Given After Epinephrine if Still in Arrest After Next Rhythm Check
- *See Antiarrhythmic Pharmacology
- Epinephrine
- Adjuncts:
- Calcium Chloride
- Dose: 1 g IV
- Vasopressor and Inotropic Effects
- Not Routinely Given but May Be Considered
- Sodium Bicarbonate
- Dose: 50-100 mEq IV (1-2 Amps/Ampules)
- Can Mitigate the Effects of Acidosis and Hyperkalemia
- Not Routinely Given but May Be Considered if Concerned for Significant Acidosis or Hyperkalemia
- Calcium Chloride
Cardiac Arrest Management Algorithm:
Immediate CPR and Oxygen
Check Rhythm Every 2 Minutes:
- VF/pVT:
- Defibrillate
- Alternate Epinephrine and Amiodarone After Each Check
- PEA/Asystole:
- Epinephrine After Every Other Check
Adjuncts:
- Calcium Chloride
- Sodium Bicarbonate
