Third Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block)
Third Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block)
David Ray Velez, MD
Complete AV Dissociation with Total Interruption of Impulse Transmission from the Atria to the Ventricles
- Essentially the Endpoint of Second Degree AV Block
- High Risk for Hemodynamic Instability and Cardiac Arrest
EKG Pattern
- P Wave and QRS Complex are Completely Independent
- The P-P Interval Remains Relatively Constant
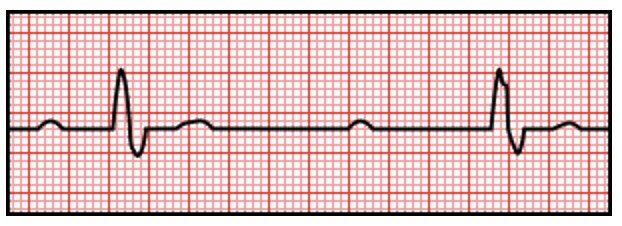
Third Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block)
Pathologic Causes
- Myocardial Infarction (MI)
- Electrolyte Derangements
- High Resting Vagal Tone – Athletes
- Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Post-Cardiac Surgery
- Medications (Beta-Blockers, Calcium Channel Blockers, Digoxin, etc.)
Treatment
- Unstable: Atropine and Temporary (Transcutaneous) Cardiac Pacing
- Atropine Dose: 1.0 mg IV, Repeated Every 3-5 Minutes as Needed (Up to a Total Dose of 3 mg)
- *Atropine is Unlikely to Work in Third Degree AV Block Because the Transmission is Completely Blocked and Therefore Not Impacted by the Effects of Atropine (Increased SA Node Firing and Conduction Through the AV Node)
- Additional Options if Remains Unstable After Pacing: Dopamine or Dobutamine Infusion
- *See Antiarrhythmic Pharmacology
- Stable: Permanent (Transvenous) Pacemaker Placement


