Pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Materials
Materials
- Needle:
- Adults: 7-9 cm 18 Gauge Spinal Needle
- Infants/Small Pediatrics: Smaller Needle (4 cm 20 Gauge)
- Large Volume (50-100 mL) Syringe
- Leaving a Drain is Preferred (Requires a Guidewire and Catheter)
- *May Have Access to a Prepackaged Pericardiocentesis Kit
- *Can Use the Material in a Prepackaged Central Line Kit or Small Percutaneous Chest Tube Kit if Necessary
- Prefer to Use an Ultrasound if Available
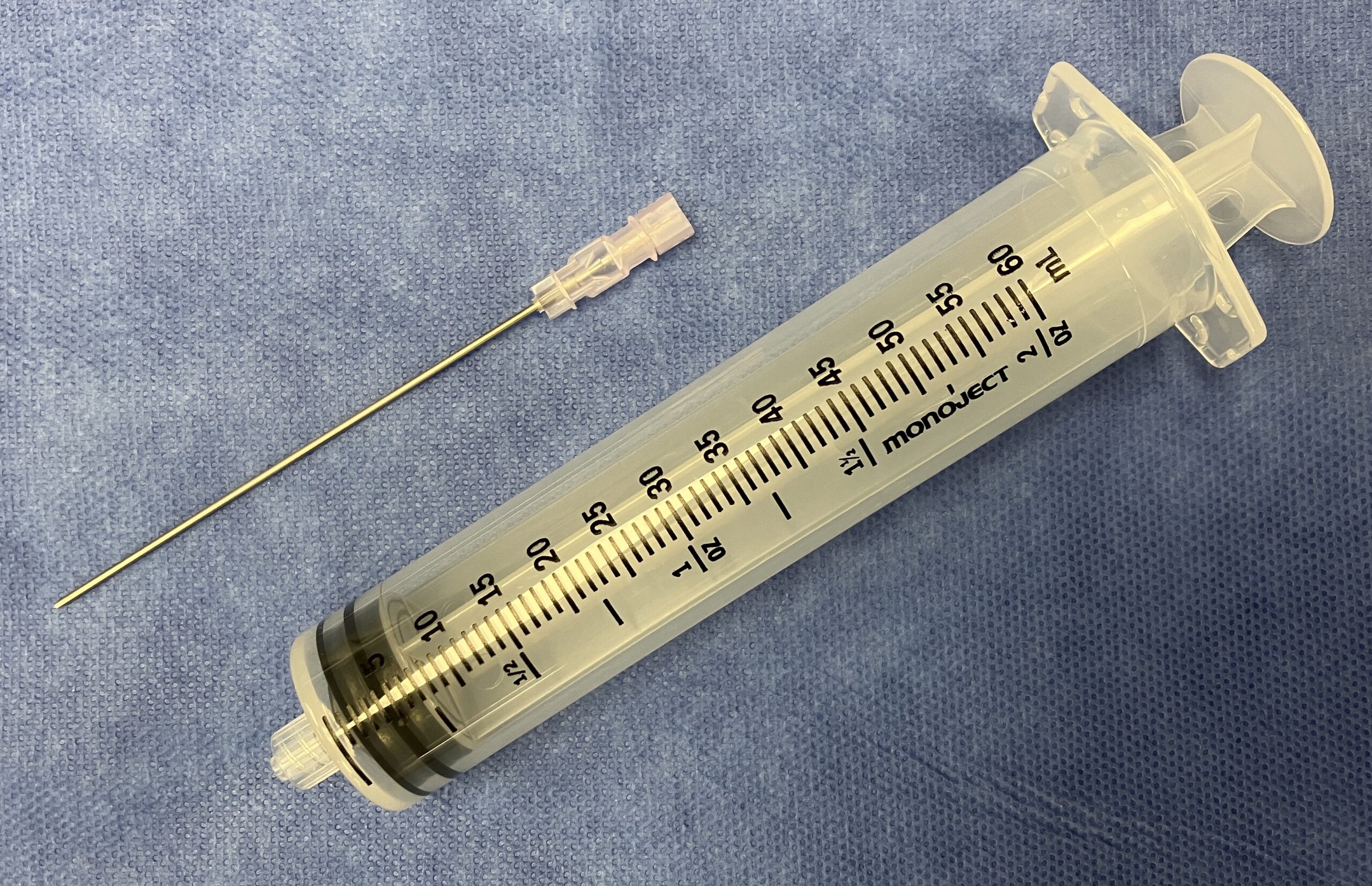
Minimum Equipment for Pericardiocentesis: Large 18 Gauge Spinal Needle and Syringe
Technique
Position and Preparation
- Supine
- Head-of-Bed at 30-45 Degrees (Supports Dependent Fluid Pooling and Brings the Heart Nearer the Chest Wall)
- Prepared Skin with Chlorhexidine or Iodine
- Drape in Standard Fashion
- Inject the Skin with Local Anesthetic
- *Avoid Sedation – Can Rapidly Decompensate Upon Induction
Approaches
- Subxiphoid Approach
- Insertion: Under the Xiphoid Process
- Aim: 30-45 Degree Angle Toward the Left Shoulder
- Parasternal Approach
- Insertion: Left 5th/6th Rib Space
- Aim: Perpendicular
- Apical Approach
- Insertion: Left 5th-6th Rib Space, 5 cm Lateral
- Aim: 30-45 Degree Angle Toward the Right Shoulder
Procedure
- Perform Under Real-Time Ultrasound Guidance (Preferred) or by Using Landmarks Alone
- Insert Needle with Negative Pressure Applied to the Syringe Until Blood is Aspirated
- Remove the Syringe and Place a Pericardial Drain by Seldinger Technique
- Insert a Guidewire Through the Needle and then Remove the Needle
- Dilate the Tract Over the Guidewire
- Insert a Catheter Over the Guidewire
- Remove the Guidewire
- *Pericardial Placement Should Be Confirmed Prior to Drain Placement
- Secure the Drain to the Skin with a Suture an Attach the Drain to a Collection Device
Confirm Pericardial Placement
- Directly Visualize by Ultrasound
- Inject “Agitated” Saline to Assist in Confirmation by Ultrasound
- Rapidly Mix 9 cc Saline with 1 cc Air Between Two Syringes Immediately Prior to Injection)
- Layering of Contrast Outside the Heart Confirms Pericardial Placement
- Put Some Aspirated Fluid into a Container and Monitor for Clotting
- Interventricular Blood Will Clot
- Pericardial Blood Will Not Clot (Due to the Intrinsic Fibrinolytic Activity of the Pericardium)
- Send Aspirated Fluid for a Blood Gas
- Interventricular Blood will Have the Respective Blood Gas Values
- Pericardial Blood will Have a Lower pH, Lower PaO2, and pCO2
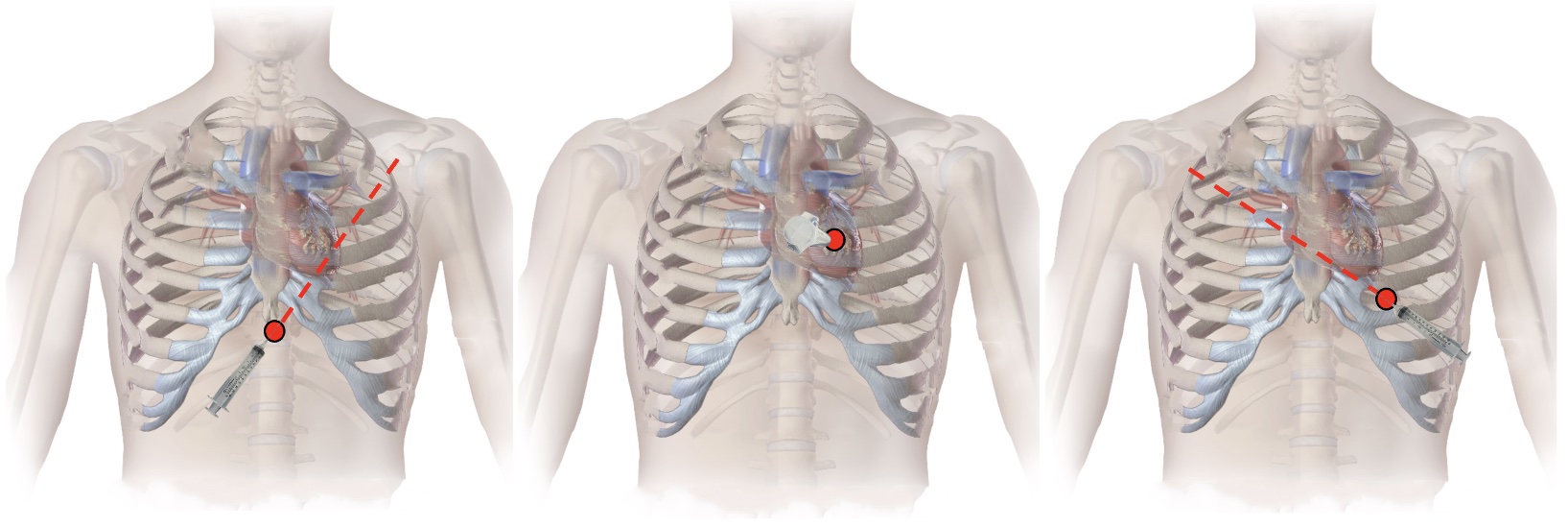
Pericardiocentesis Approaches: Subxiphoid (Left), Parasternal (Middle), and Apical (Right) 2
Complications
Complications
- Bleeding
- Infection (Pericarditis)
- Arrhythmia
- PVC’s are Most Common
- May Seen a Vasovagal Bradycardia – Responds to Atropine
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumopericardium
- Cardiac Injury or Perforation
- Liver Injury
- Stomach Injury
References
- COVER: BruceBlaus. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- BruceBlaus. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)


