Subxiphoid Pericardial Window
Subxiphoid Pericardial Window
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Background
Definition: A Surgical Procedure to Create an Opening in the Pericardium to Evaluate for Pericardial Fluid/Blood
Used in Trauma as a Diagnostic Tool to Evaluate for Cardiac Injury (Not Therapeutic)
- *See Cardiac Laceration
- Less Commonly Preformed Now; But Consider if FAST is Equivocal
Outside of Trauma it Can be Used to Drain a Pericardial Effusion
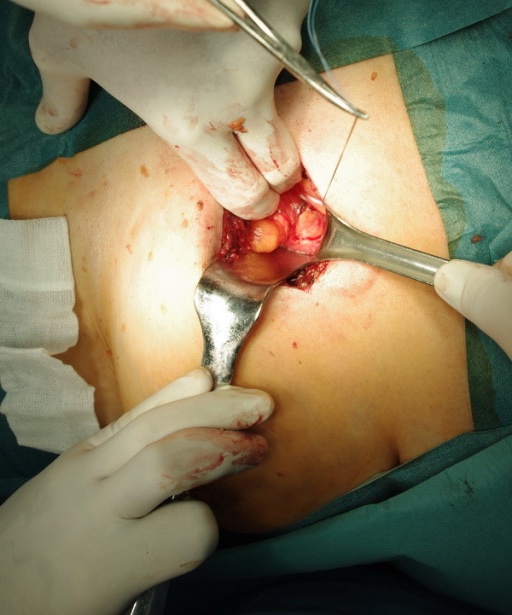
Subxiphoid Procedure
Procedure
- Incision: 8-10 cm Midline Incision Over the Xiphoid
- Dissect Toward the Cardiac Impulses to Find the Pericardium
- May Require Resection of the Xiphoid Tip if Obstructing the View
- Will See Preperitoneal Fat but Take Care Not to Enter the Peritoneum
- Grasp the Pericardium Between Two Alice Clamps
- Make a 1-2 cm Longitudinal Incision in the Pericardium Between the Clamps
- Ensure Adequate Local Hemostasis Before Making a Pericardial Incision to Avoid Confusing the Interpretation of Results
- Flood the Field/Pericardial Sac with Fluid
- Suction Fluid and Examine the Quality
- If Negative: Close the Pericardium and Skin
Results
- Positive: Bloody Fluid (Caution: Clotted Blood May Be Dry on Incision)
- Negative: Clear or Straw-Colored Fluid
Hemopericardium (Positive Pericardial Window) Generally Necessitates Median Sternotomy to Evaluate and Manage Cardiac Injury
Pericardial Window 1
Alternative Approaches
Anterior Parasternal Pericardial Window – Performed Through a 6-8 cm Vertical/Curvilinear Incision Along the Left Parasternal Border to Create an Anterior “Mini-Thoracotomy” at the 4th-5th Rib Space to Access and Create the Pericardial Window
Transdiaphragmatic Pericardial Window – Can Be Performed During Laparotomy for Other Reasons by Creating an Incision Through the Diaphragm to Access and Create the Pericardial Window
Anterolateral Left Thoracotomy – Can Be Performed During Thoracotomy for Other Reasons to Access and Create the Pericardial Window
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) Pericardial Window – A Minimally Invasive Technique Using a Thoracoscope Inserted Through into the Left Pleural Space to Access and Create the Pericardial Window (Not Used in Trauma)
References
- Toth I, Szucs G, Molnar TF. Mediastinoscope-controlled parasternal fenestration of the pericardium: definitive surgical palliation of malignant pericardial effusion. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012 Jun 19;7:56. (License: CC BY-2.0)
