Lung Volumes
Lung Volumes
David Ray Velez, MD
Also Known as “Lung Capacities”
Definition: The Volume of Air Moved the Lungs Through Different Phases of the Respiratory Cycle
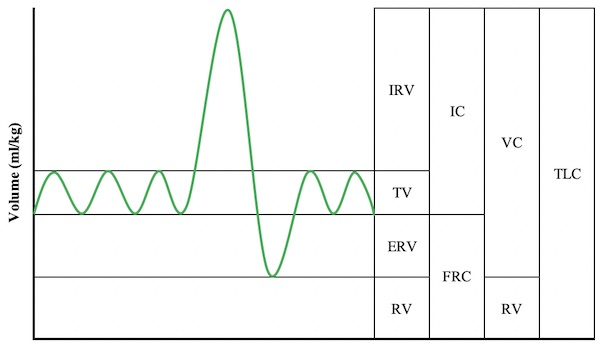
Base Volumes
- Tidal Volume (TV): Normal Breath
- Inspiratory Residual Volume (IRV): Maximum Extra Inhaled Beyond a Normal Breath
- Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): Maximum Extra Exhaled Beyond a Normal Breath
- Residual Volume (RV): Volume Unable to Exhale Out of the Lung
Summative Volumes
- Inspiratory Capacity (IC): The Maximum Volume Able to Be Inhaled (Including TV and IRV)
- IC = TV + IRV
- Functional Residual Capacity (FRC): The Volume Functionally Not Exhaled During a Breath Without Forced Expiration
- FRC = ERV + RV
- Causes of Increased FRC: PEEP
- Causes of Decreased FRC: Surgery, ARDS, Trauma
- Vital Capacity (VC): The Maximum Volume Able to Be Functionally Moved in and Out of the Lungs During a Breath
- VC = TV + IRV + ERV = TLC – RV
- Also Known as “Functional Vital Capacity (FVC)”
- Total Lung Capacity (TLC): The Total Possible Capacity of the Lungs During a Maximal Inhalation
- TLC = VC + RV
Lung Volumes
