Hemothorax (HTX)
Hemothorax (HTX)
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Definition
Hemothorax (HTX): Gas within the Pleural Space Between the Lungs and Chest Wall
Occult Hemothorax: A Hemothorax Seen on CT but Not Visible on Chest X-Ray
- Minimum Volume Required to Be Seen on Standard Upright Chest X-Ray: 300 cc
Causes
- Traumatic Hemothorax: Hemothorax Due to Trauma
- By Far the Most Common Cause
- Iatrogenic Hemothorax: Hemothorax Due to Medical Interventions (Surgery, Catheter, Biopsy, etc.)
- Spontaneous Hemothorax: Hemothorax without an Obvious Cause
Size
- Small (Minimal): < 300-400 cc
- Medium: 400-1,000 cc
- Large (Massive): > 1,000 cc (1 L)
Delayed Hemothorax (DHTX): Hemothorax that Develops After Initial Imaging is Negative
- Predominantly Affect the Elderly
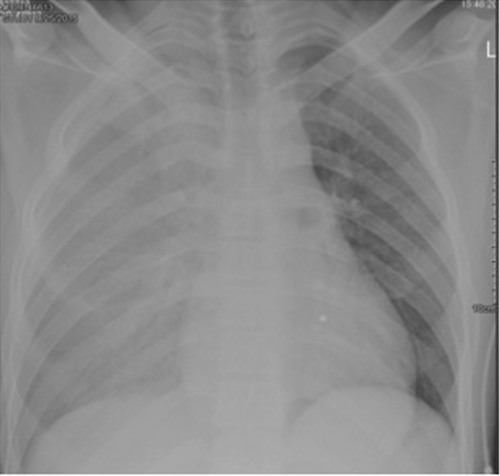
Hemothorax (HTX) 1
Diagnosis
Hemothorax is Most Often Diagnosed on Imaging (CT is the Gold Standard)
Physical Exam Findings
- Unequal Breath Sounds (Decreased/Absent on the Affected Side)
- Dullness to Percussion
- Decreased Chest Wall Movement
- Tracheal Deviation – Away from the Affected Side
- Respiratory Distress
- Tachypnea
- Hypoxemia
- Cyanosis
- Hypotension and Narrow Pulse Pressure
Treatment
General Management
- Asymptomatic and Small/Occult: Observation
- Repeat CXR in 6 Hours to Monitor Progression
- Symptomatic or Medium-Large: Chest Tube
- *See Thoracostomy Tube (Chest Tube)
- Preferred Tube Size: 24-28 Fr
- A Second Chest Tube May Be Required if Not Adequately Draining After Initial Insertion (Not for Retained Hemothorax)
Thoracic Irrigation (Thoracic Lavage)
- Definition: Irrigation of the Thorax Through the Chest Tube Upon Insertion
- Reduces the Risk of Retained Hemothorax and Secondary Interventions
- Irrigation Volumes ≥ 1,000 mL Normal Saline are Preferred – Shown Shorter Hospital Length of Stay
Thoracotomy Indications
- Initial Loss > 1,500 cc
- Continual Loss > 200 cc/hr for 4 Hours
- *Some Say 250 cc/hr for 3 Hours
- CAUTION: A Dramatic Decrease in Volume Can Be Due to Complete Evacuation but Can Also Occur Due to Clotting within the Chest Tube
Retained Hemothorax
Retained Hemothorax (rHTX) Definition: Hemothorax that Has Failed to Completely Evacuate with Chest Tube Drainage After 2-3 Days
Occurs in 5-10% of Cases – May Be Decreased by Thoracic Irrigation
Risk Factors
- High Initial Volume of Blood
- High Injury Severity Score (ISS)
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Multiple Rib Fractures
- Pneumonia (PNA)
- Prolonged Time of Chest Tube Drainage
- Low Hematocrit
Retained Hemothorax is a High Risk of Fibrothorax and Empyema
Management
- Additional Chest Tubes are Generally Ineffective
- Should Obtain a CT for Definitive Diagnosis and Evaluation Before Surgery or Fibrinolytic Therapy
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
- The Primary Treatment for Retained Hemothorax
- Surgery Timing: Should Be Done Early within 7 Days (Before Loculations Can Develop)
- Intrapleural Fibrinolytic Therapy
- Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA) – Activates Plasmin to Breakdown Thrombin and Decrease Fluid Viscosity
- Regimen:
- 50 mg tPA in 100 mL NS Instilled into the Chest Tube
- Chest Tube Clamped for One Hour and Rolled to Distribute
- Repeat Daily Until Resolved
- Most Studies Show > 80% Success and < 7% Bleeding Risk
- Regimen:
- Dornase Alfa (DNase/Pulmozyme) – Nebulized to Breakdown DNA and Thin Mucous in Cystic Fibrosis
- Instilled Through Chest Tubes in Addition to tPA (tPA-DNase) for Parapneumonic Effusions/Empyema
- No Proven Benefit When Added for Retained Hemothorax (Unless Progressed to Empyema)
- Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA) – Activates Plasmin to Breakdown Thrombin and Decrease Fluid Viscosity
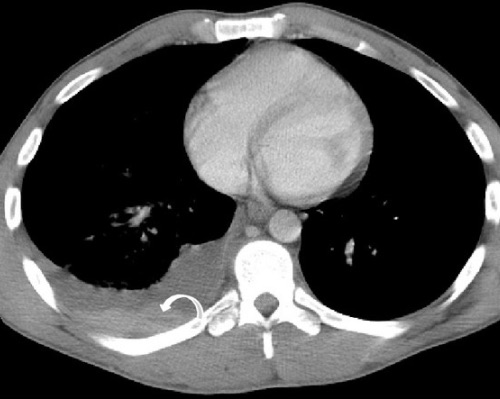
Retained Hemothorax with Hematocrit Sign 2
References
- Mishra B, Joshi MK, Kumar S, Kumar A, Gupta A, Rattan A, Sagar S, Singhal M, Misra MC. Innocuous cardiac gunshot that proved fatal: A bitter lesson learned. Chin J Traumatol. 2017 Apr;20(2):122-124. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)
- Palas J, Matos AP, Mascarenhas V, Herédia V, Ramalho M. Multidetector computer tomography: evaluation of blunt chest trauma in adults. Radiol Res Pract. 2014;2014:864369. (License: CC BY-4.0)
