Dynamic Hyperinflation (DHI)
Dynamic Hyperinflation (DHI)
David Ray Velez, MD
Definitions
- Dynamic Hyperinflation (DHI): Increase in End-Expiratory Lung Volume (EELV) Due to Airflow Limitations with Increased Minute Ventilation
- Air Trapping (Air Stacking): Hyperinflation Due to Incomplete Exhalation
- Auto PEEP (Intrinsic PEEP/PEEPi): Increased PEEP from Hyperinflation
- *Most Commonly Associated with COPD Exacerbation, Asthma, and ARDS
Causes
- Low Expiratory Time
- Excessively High Minute Ventilation (High Tidal Volume or Respiratory Rate)
- *Increasing Vt or Rate for Hypercarbia Can Actually Worsen Hypercarbia in These Patients
- Increased Expiratory Airflow Resistance
- Bronchospasm (COPD/Asthma)
- Secretions
- Narrowed/Kinked Endotracheal Tube
- Increased Compliance (Reduced Elastic Recoil)
- Persistent Respiratory Muscle Inspiratory Activity During Expiration
- Ventilator Dyssynchrony
Complications
- Alveolar Over-Distention and Barotrauma
- Additional Injury Due to the Inflammatory Response Which Can Cause Airway Edema and Mucous Plugging
- Decreased Compliance
- Decreased Venous Return, Preload, and Cardiac Output
Identification and Diagnosis
- Ventilator Graphics Show Airflow Failing to Return to Zero at End-Expiration
- End-Expiratory Hold Maneuver
- Used to Measure Auto PEEP
- The Expiratory Circuit is Occluded or Paused for 3-5 Seconds at the End of an Expiration
- The Alveolar Pressure Then Equilibrates with the Airway Pressure
- Escaping Trapped-Air Will Increase Airway Pressure on the Ventilator (Auto PEEP) Above the Set PEEP
Management
- Immediately Disconnect the Ventilator to Deflate if Concerned for Severe Auto PEEP Causing Cardiovascular Collapse
- Treat Any Underlying Pathology
- Decrease Inspiratory Time or Increase Expiratory Time (Decreased I/E Ratio)
- Increase Inspiratory Flow Rate (IFR)
- Decrease Tidal Volume
- Decrease Respiratory Rate
- *Allow for Permissive Hypercapnia (Avoid pH < 7.20 – Risk for Hemodynamic Instability)
- Bronchodilators
- Improve Ventilator Synchrony
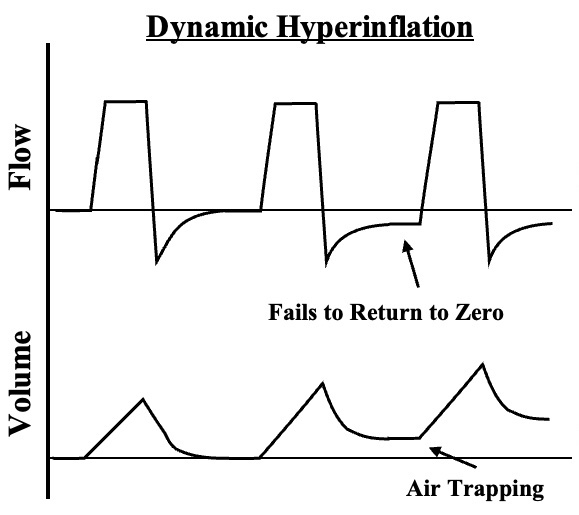
Flow and Volume Graphs Demonstrating Dynamic Hyperinflation
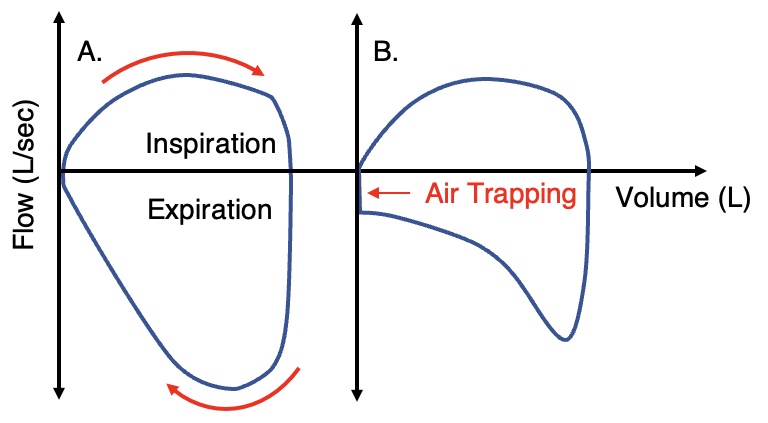
Flow-Volume Loops on a Ventilator: A. Normal; B. Obstructive Pattern with Air Trapping (Fails to Return to Zero)
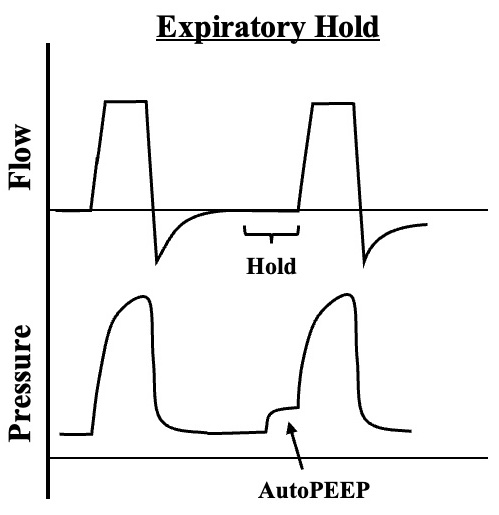
Expiratory Hold Maneuver Demonstrating Dynamic Hyperinflation


