Coagulation Cascade
Coagulation Cascade
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Coagulation Cascade
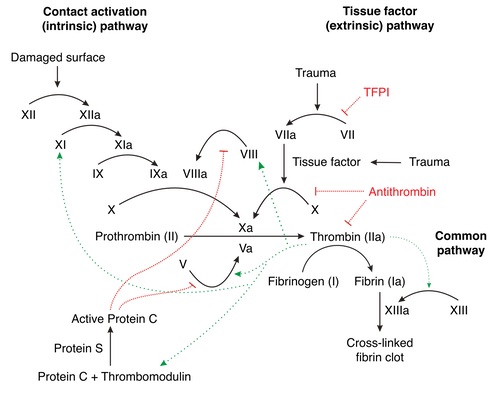
An Initial Injury Induces Vasoconstriction, Platelet Adhesion, and Thrombin Release
- Initiates the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Coagulation Pathways
Intrinsic Pathway
- Initiated By: Exposed Collagen, Pre-Kallikrein, HMW Kininogen
- Pathway:
- Activated Factor XII Activates Factor XI
- Activated Factor XI Activates Factor IX
- Activated Factor IX and VIII Activates Factor X
- Associated Factors: Factor 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12
Extrinsic Pathway
- Initiated By: Tissue Factor (From Trauma and Injured Cells)
- Pathway:
- Activated Factor VII Activates Factor X
- Associated Factors: Factor 7 and 10
Common Pathway
- Initiated By: Intrinsic or Extrinsic Pathways
- Prothrombin Complex
- Components: Activated Factor X, Factor V, Platelet Factor 3, and Prothrombin
- Converts Prothrombin (Factor II) to Thrombin
- Thrombin (Factor IIa)
- Converts Fibrinogen (Factor I) to Fibrin
- Also Activates Factors V, VIII, and XIII
- Also Activates Platelets
- Fibrin (Factor Ia)
- Links Platelets to Form a Platelet Plug
- Binds GpIIb/IIIa
- Fibrin Stabilizing Factor (Factor XIII)
- Activated by Thrombin
- Crosslinks Fibrin to Improve Clot Stability
Factor Synthesis
- Factor VIII is Produced in the Endothelium with vWF
- All Other Factors are Produced in the Liver
- Vitamin K Dependent Factors: Factor II, VII, IX, X, Protein C, and Protein S
- Produced Through Gamma Carboxylation of Glutamate Residues
- Half-Life of Vitamin K-Dependent Factors:
- Factor II: 60-72 Hours
- Factor VII: 4-6 Hours (Shortest)
- Factor IX: 21-30 Hours
- Factor X: 48-72 Hours
- Protein C: 6-8 Hours (Second Shortest)
- Protein S: 30-60 Hours
Coagulation Cascade 1
Mediators of Platelet Aggregation
Von Willebrand Factor (vWF)
- Produced by Endothelium
- Binds to Exposed Collagen at Sites of Vascular Injury for Platelet Adhesion
- Promotes Platelet Aggregation Through GPIb (Most Efficient When Under Shear Stress)
Thromboxane A2 (TXA2)
- Produced by Activated Platelets
- Stimulates Platelet Aggregation
- Triggers Calcium Release in Platelets (Exposes GpIIb/IIIa Receptor for Fibrin)
- Also Induces Vasoconstriction
Prostacyclin (PGI2/Prostaglandin I2)
- Produced by Endothelium
- Inhibits Platelet Aggregation
- Increases cAMP in Platelets
- Also Induces Vasodilation
Mediators of Anticoagulation
Inhibitory Enzymes
- Antithrombin III (AT-III)
- Inhibits Thrombin (IIa) and Factor Xa
- Activated by Heparin
- Activated Protein C (APC)
- Degrades Factors Va and VIIIa
- Protein S
- Cofactor for Protein C
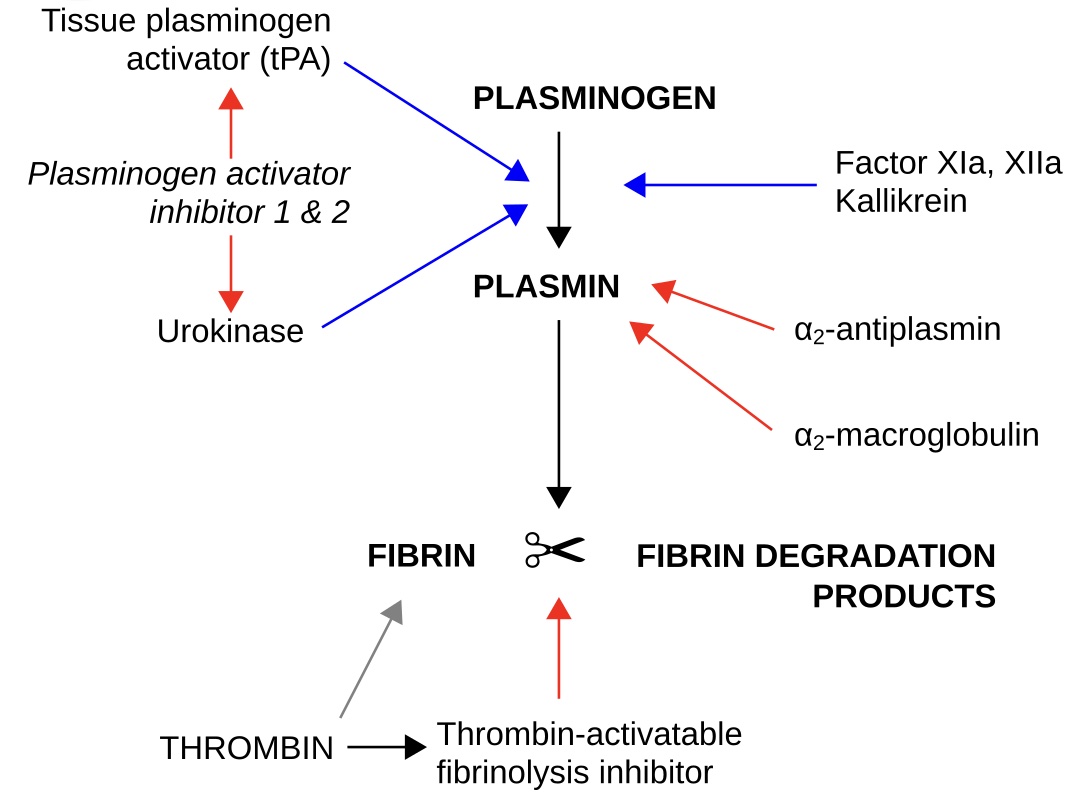
Fibrinolysis
- Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
- Released from Endothelium
- Converts Plasminogen to Plasmin
- Inhibited by Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor (PAI-1 and PAI-2)
- Plasmin
- Function:
- The Most Important Clotting Inhibitor in Plasma
- Degrades Fibrin (Platelet Plug) into Fibrin Degradation Products
- Also Degrades Factors V, VIII, and Fibrinogen
- Plasminogen is Converted to Active Plasmin by tPA, Streptokinase, and Urokinase
- Inhibited by α-2 Antiplasmin
- Released from Endothelium
- Decreased Production in Liver Cirrhosis
- Function:
Fibrinolysis 2
References
- Joe D. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
- Jfdwolff . Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
