Brain Death
Brain Death (Death by Neurologic Criteria)
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Diagnosis
Definition: A Permanent, Irreversible, and Complete Loss of Brain Function
Determination of Brain Death is Primarily a Clinical Diagnosis and Can Be Done with a Clinical Exam that Demonstrates Coma, Brainstem Areflexia, and Apnea
Mandatory Criteria to Consider the Diagnosis
- Must Have Neuroimaging Consistent with the Mechanism and Severity
- No Spontaneous Respirations
- No Response to Pain/Noxious Stimulation
- No Cranial Nerve Reflexes
- *Can Still Have Spinal Cord/Deep Tendon Reflexes
Criteria that Exclude the Diagnosis
- Hypothermia
- Hypotension (Stable Dose Vasopressors are Acceptable)
- Significant Metabolic Derangements (Electrolytes, Acid-Base, or Endocrine)
- Depressant Drugs
Definitive Testing (If All Other Criteria are Met)
- Preferred Definitive Test: Apnea Test
- Ancillary Testing:
- Indications:
- Unstable and Unable to Tolerate Time Off Ventilator (Hypoxic Respiratory Failure, etc.)
- High Cervical Spine Injury that May Inhibit Phrenic Nerve Function
- Unable to Perform All Cranial Nerve Reflexes (C-Spine Fracture, Severe Eye/Ear Injury, etc.)
- Acceptable Testing:
- Four-Vessel Cerebral Angiogram
- Nuclear Cerebral Scintigraphy
- Transcranial Doppler
- Unacceptable Tests: EEG, CTA, MRI/MRA
- Indications:
Note: Laws are Different in Different States and Physicians Should Be Aware of State, Local, and Facility Regulations
Pediatrics Often Have Additional Requirements Such as a Second Examiner with Mandatory Time Between Examinations
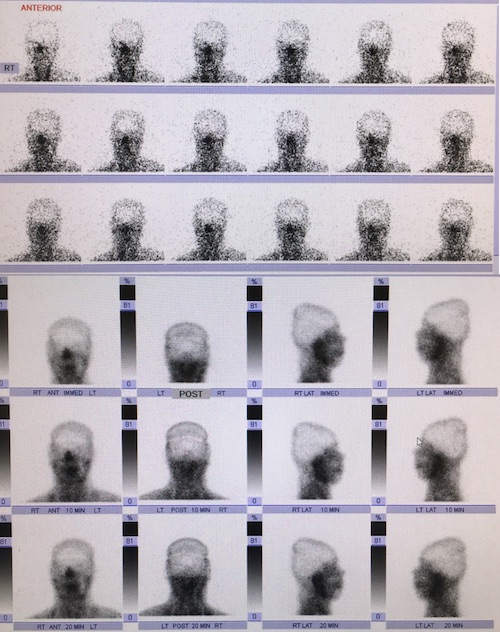
Brain Death by Nuclear Cerebral Scintigraphy
Cranial Nerve Reflexes
Pupillary Light Reflex
- Test: Light Shown into the Eye
- Normal Reflex: Prompts Pupil Constriction
- Absent Reflex: Pupil Does Not Constrict
Corneal Reflex
- Test: Cornea Touched with Cotton Swab or Saline
- Normal Reflex: Prompts Blinking
- Absent Reflex: Does Not Blink
Gag Reflex
- Test: Touching the Posterior Pharyngeal Wall
- Normal Reflex: Prompts Palate Elevation
- Absent Reflex: No Palate Elevation
Cough Reflex
- Test: Tracheal Suctioning
- Normal Reflex: Prompts Coughing
- Absent Reflex: Does Not Cough
Oculocephalic (Doll’s Eyes) Reflex
- Test: With Eyes Held Open the Head is Briskly Turned Side-to-Side and Held at the End of the Turn
- Normal Reflex: Eyes Rotate to the Opposite Side of Head Rotation (Continue to Look Forward)
- Absent Reflex: Eyes Do Not Rotate
- *Must First Ensure that the Cervical Spine is Clear and May Be Unable to Perform if a Collar is in Place
Oculovestibular (Cold Caloric) Reflex
- Test: With Head Elevated at 30 Degrees, 200 cc of Ice Water is Instilled into the External Ear Canal
- Normal Reflex: Nystagmus with Eye Deviation to the Tested Ear
- Absent Reflex: No Nystagmus Seen
Apnea Test
Test
- Preoxygenate with 100% O2 for at Least 10 Minutes Before Starting
- Ensure CO2 Normal (35-45 mmHg) by ABG Before Starting
- Disconnect the Ventilator for 10 Minutes
- Continue to Deliver O2 During the Test
- Monitor for Spontaneous Respirations During the Test
- Repeat an ABG After 10 Minutes
Positive Test Result (Requires All for Diagnosis of Brain Death)
- (1) No Respirations are Seen
- (2) Arterial pH < 7.30
- (3) PaCO2 ≥ 60 mmHg AND Increases by ≥ 20 mmHg
- If Known the Have Chronic CO2 Retention: Increase by ≥ 20 mmHg Above the Known Chronic Elevated Level
- *Previously “OR” Prior to 2023 Guidelines
- *Can Continue Testing Beyond 10 Minutes and Repeat ABG Every 2 Minutes if ABG Thresholds are Not Met
Indications to Abort Apnea Testing
- Hemodynamic Instability: SBP < 100 mmHg or MAP < 75 mmHg Despite Titration of Vasopressors, Inotropes, or Fluids
- Hypoxia: Progressive Decrease in SpO2 < 85%
- Cardiac Arrhythmia with Hemodynamic Instability
