Pulmonary Aspiration
Pulmonary Aspiration
David Ray Velez, MD
Definitions
- Aspiration: Entry of Material into the Larynx and Lower Respiratory Tract
- Includes Oropharyngeal Contents (Food/Drink) or Gastric Contents
- Aspiration (Chemical) Pneumonitis: Inflammatory Reaction in the Lower Airways in Response to Aspiration
- Independent of Infection
- Mediated by Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α and IL-8)
- Mendelson’s Syndrome – Aspiration Pneumonitis that Occurs During Anesthesia, Particularly During Pregnancy
- Aspiration (Bacterial) Pneumonia: Acute Bacterial Infection Due to Aspiration
- Most Common Site: Superior Segment of Right Lower Lobe (RLL)
Risk Factors
- Dysphagia
- Head, Neck, and Esophageal Tumors
- Esophageal Stricture
- Esophageal Motility Disorders
- COPD
- Seizures
- Degenerative Neurologic Disease (Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s Disease, Dementia)
- Altered Mental Status
- Stroke
- Antipsychotic Medication
- Cardiac Arrest
Diagnosis
- Primary a Clinical Diagnosis (Based on Clinical History, Exam, and Chest X-Ray)
- Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) May Be Used to Distinguish Pneumonia from Pneumonitis
Treatment
- Treatment: Primarily Supportive Therapy
- Antibiotics: Generally Only Indicated for Defined Pneumonia
- Aspiration or Aspiration Pneumonitis Alone Do Not Require Prophylactic Antibiotic Therapy, Even if Radiographic Infiltrate Present
- May Consider Empiric Antibiotic Treatment in Severe Cases
- Bronchoscopy: Not Routinely Required
- Consider if a Large-Volume Aspiration was Witnessed with Concern for Particulate Matter in the Airway
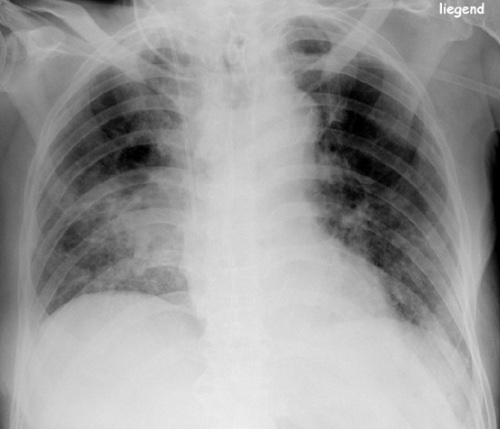
Aspiration of RLL 1
References
- Gossner J, Nau R. Geriatric chest imaging: when and how to image the elderly lung, age-related changes, and common pathologies. Radiol Res Pract. 2013;2013:584793. (License: CC BY-Unspecified)
