Airway Assessment
Airway Assessment
David Ray Velez, MD
Table of Contents
Assessment of the Difficult Airway
Difficult Airway: A Clinical Condition in Which There is Difficulty with Face Mask Ventilation, Supraglottic Ventilation, or Endotracheal Intubation
- Review History for Prior Intubation Attempts to Understand Prior Grades, Difficulties, and Necessary Adjuncts
- Measures to Predict a Difficult Airway are Neither Sensitive nor Specific
- Airway Assessment May Be Contraindicated in Emergency Scenarios
Indicators of Difficult Intubation
- History of Difficult Intubation
- Interincisor Distance < 3 cm
- Thyromental Distance < 3 Fingerbreadths (About 7 cm)
- High, Arched, Narrow Palate
- Mallampati Class III-IV
- Inability to Bring Mandibular Incisors Anterior the Maxillary Incisors
- *Morbid Obesity is a Predictor of Difficult Mask Ventilation but Not Independently Associated with Difficult Intubation
LEMON Approach to Airway Assessment
- L: Look Externally
- Level of Consciousness
- Obesity
- Bearded
- Craniofacial Deformity
- E: Evaluate 3-3-2 Rule
- Interincisor Distance: Distance Between the Upper and Lower Teeth
- Distance < 3 Fingerbreadths Indicates a Difficult Airway
- Hyoid-to-Mental Distance: Distance Between the Hyoid Bone and Mental Protuberance of the Mandible
- Distance < 3 Fingerbreadths Indicates a Difficult Airway
- Thyroid-to-Hyoid Distance: Distance Between the Thyroid Cartilage and Hyoid Bone
- Distance < 2 Fingerbreadths Indicates a Difficult Airway
- Interincisor Distance: Distance Between the Upper and Lower Teeth
- M: Mallampati Score
- Class III-IV Indicates Difficult Intubation
- *See Classification/Scoring Below
- O: Obstruction
- Epiglottitis
- Head/Neck Cancer
- Neck Hematoma
- Foreign Body
- Thermal Injury
- N: Neck Mobility
- Evaluate for Neck Extension if Able
- May Be Unable to Move in Trauma Patient (Cervical Collar)
6-D Approach to Airway Assessment
- 1D: Disproportion
- Mallampati Class
- Enlarged Tongue
- Airway Swelling
- Airway Trauma
- Tracheal Deviation
- 2D: Distortion
- Neck Mass
- Neck Hematoma/Abscess
- Prior Surgical Airway
- 3D: Decreased Thyromental Distance
- Thyromental Distance < 7 cm (3 Fingerbreadths)
- 4D: Decreased Interincisor Distance
- Interincisor Distance < 3 Fingerbreadths
- 5D: Decreased Range of Motion
- Limited Neck Extension
- Cervical Collar
- Cervical Contracture or Burns
- Short/Thick Neck
- 6D: Dental Overbite
- Overbite
- Large Angled Teeth Disrupting Alignment
Classification/Scoring
Cormack-Lehane Laryngoscopy Classification
- View During Direct Laryngoscopy Associated with Risk for Difficult Intubation
- Classification:
- Grade 1: Full Glottis
- Grade 2: Partial Glottis
- 2a: Partial Glottis
- 2b: Arytenoids Only
- Grade 3: Epiglottis, No Glottis
- Grade 4: No Epiglottis or Glottis
- Class ≥ 2b Indicates Difficult Intubation
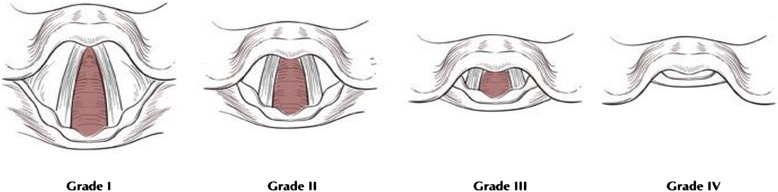
Cormack-Lehane Classification 1
| Grade | Percentage of Patients | Percentage with Difficult Intubations |
| 1 | 74% | < 1% |
| 2a | 21% | 13% |
| 2b | 3% | 65% |
| 3 | 2% | 80% |
| 4 | < 1% | 100% |
Mallampati Score (Modified)
- External View of the Oral Cavity Used to Estimate Risk for Difficult Intubation
- Modified Classification:
- Class I: Visualize Soft Palate, Entire Uvula, Fauces, and Tonsillar Pillars
- Class II: Visualize Soft Palate, Partial Uvula, and Fauces
- Class III: Visualize Soft Palate and Base of Uvula
- Class IV: Visualize Only Hard Palate
- Class III-IV Indicates Difficult Intubation
- Positive Predictive Value is Only 21-50%
- *Worse Prognostic Value than the Cormack-Lehane Classification
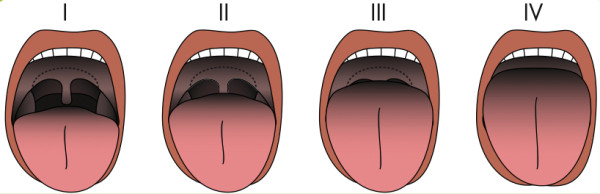
Mallampati Score 2
Difficult Bag Mask Ventilation (BMV)
MOANS Mnemonic
- Mask Seal (Beards, Crusted Blood on Face, Craniofacial Deformity)
- Obesity
- Age > 55 Years
- No Teeth
- Sleep Apnea/Stiff Lungs (COPD, Asthma, ARDS)
BONES Mnemonic
- Beard or Other Cause of Difficult Mask Seal
- Obesity
- No Teeth
- Elderly (Age > 55 Years)
- Sleep Apnea/Stiff Lungs (COPD, Asthma, ARDS)
ROMAN Mnemonic
- Restriction (Poor Lung Compliance – ARDS, etc.)
- Obesity or Obstruction (Sleep Apnea)
- Mask Seal (Beards, Crusted Blood on Face, Craniofacial Deformity)
- Age > 55 Years
- No Teeth
Difficult Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Placement
RODS Mnemonic
- Restricted Mouth Opening
- Obstruction
- Disrupted/Distorted Airway
- Stiff Lungs or C-Spine
Difficult Cricothyroidotomy
SHORT Mnemonic
- Surgery
- Hematoma or Abscess
- Obesity
- Radiation Distortion or Deformity
- Tumor
SMART Mnemonic
- Surgery
- Mass (Hematoma, Abscess)
- Access or Anatomy (Obese, Poor Landmarks)
- Radiation Distortion or Deformity
- Tumor
References
- Zeger WG, Branecki CE, Nguyen TT, Hall T, Boedeker B, Boedeker D, Wadman MC. A description of teaching methods using an on-site instructor versus a distant site instructor to train laryngoscopy to medical students in Hanoi, Vietnam, from Omaha, Nebraska, by video communication. Int J Emerg Med. 2015 Dec;8(1):44. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Nørskov AK, Rosenstock CV, Wetterslev J, Lundstrøm LH. Incidence of unanticipated difficult airway using an objective airway score versus a standard clinical airway assessment: the DIFFICAIR trial – trial protocol for a cluster randomized clinical trial. Trials. 2013 Oct 23;14:347. (License: CC BY-2.0)
